What is Diamond Clarity?
by Admin
Posted on 30-09-2022 11:27 AM
Natural diamonds are formed in the earth’s mantle layer at a depth ranging between 80-120 miles, and they face extreme heat up to 2,200 degrees fahrenheit.
While their growth takes between one billion to three billion
years
, only the rarest diamonds emerge in perfect condition. Most often they are imperfect and contain varying amounts of internal inclusions and surface blemishes. When determining the clarity of diamonds on a clarity scale, experts will note the appearance of the diamond when it is face up, with a microscope at 10x magnification and eye visibility. However, to identify any diamond inclusions there may be, a higher power than 10x will be used.
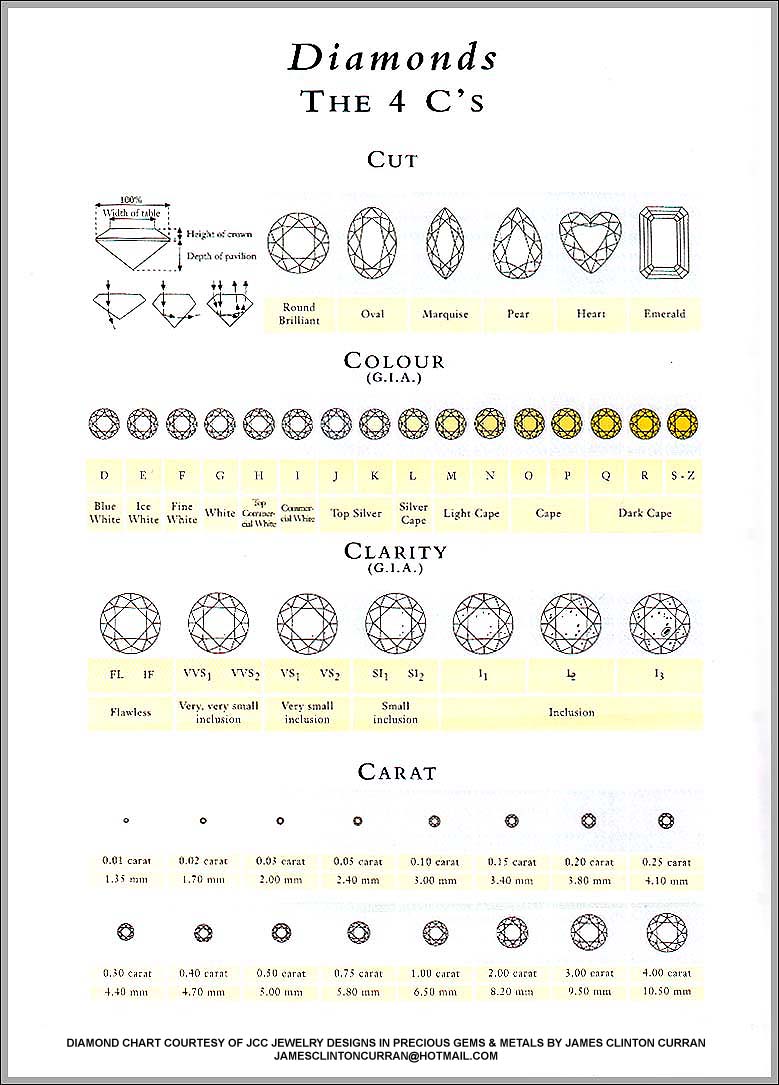
Internally flawless (if) diamonds may contain external characteristics (also known as blemishes) that are extremely difficult to view at 10x magnification on the stone's surface, if at all, whereas flawless (fl) is the best clarity of a diamond as it does not contain any inclusions or blemishes, under the scrutiny of 10x magnification.
Clarity covers all things in a stone that affect the free passage of light. Thus, gem graders consider transparency , inclusions , and surface blemishes when evaluating clarity. Many gemstones contain inclusions, including virtually all diamonds. However, some are so small they don’t impact grading. Inclusions in diamonds include things like minerals, some in crystal shapes and others in long needle shapes, and twinning wisps that form inside a stone. Gem cutters usually try to cut a piece of diamond rough to create a stone as free of inclusions as possible. Typically, inclusions can’t be removed, though some treatments try to minimize their impact in faceted gems.
Home buying diamonds with confidence 4cs of diamonds understanding diamond clarity: the 4cs of diamonds.
What is a Diamond Clarity Chart?
Diamond clarity is a qualitative metric that evaluates the visual appearance of each precious stone. The fewer inclusions and blemishes a gem has, the better its clarity grading will be.
 A diamond clarity chart is merely a chart that accurately depicts what grade of clarity your diamond is. Now, this definition may not mean much to you at first, but we’re going to take it apart and look at all the individual parts of it – and ensure that you understand it better. First of all, diamond clarity is a qualitative metric that measures quality on a particular scale, like with all other qualitatively measurable things.
A diamond clarity chart is merely a chart that accurately depicts what grade of clarity your diamond is. Now, this definition may not mean much to you at first, but we’re going to take it apart and look at all the individual parts of it – and ensure that you understand it better. First of all, diamond clarity is a qualitative metric that measures quality on a particular scale, like with all other qualitatively measurable things.
To better illustrate what you can expect in the real world, we took the liberty of putting together this diamond clarity chart (as well as a diamond color chart ) with real images of all the diamond clarity grades. The focus of this article is clarity (as you’ve already noticed), therefore, we will be fixing the rest of the factors (using almost identical other characteristics for cut and carat). The following diamond clarity chart clearly illustrates real images of gia-certified diamonds from the james allen website. Click on the images on the right to see zoomed photo close-ups of the diamonds:.
In 1953, azar shares, the jewelry industry adopted an 11-factor scale for evaluating a diamond’s clarity. From least included, to most included, the measurements are: flawless (fl), internally flawless (if), very very slightly included 1 (vvs1), very very slightly included 2 (vvs2), very slightly included 1 (vs1), very slightly included 2 (vs2), slightly included 1 (si1), slightly included 2 (si2), included 1 (i1), included 2 (i2), and included 3 (i3). "the diamond clarity chart breaks down how visible inclusions are with 10x magnification and with the unaided eye, starting with no inclusions being visible even under 10x magnification for the fl and if clarities, and ending with inclusions being visible to the unaided in the i1, i2, and i3 categories," azar says.